The synthesis of imprinted polymers based on Fe3O4 nanomaterials and the recognition of proteins†
Abstract
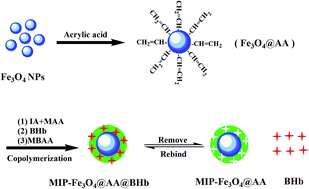
A surface molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP-Fe3O4@AA) was prepared on a magnetic material (Fe3O4@AA) surface for the selective recognition and adsorption of bovine hemoglobin (BHb). The acrylic acid (AA) monomer was directly grafted to the surface of Fe3O4 through a simple coordination reaction between the carboxyl group of AA and unsaturated iron ions (Fe3O4@AA). Then the composite of MIP-Fe3O4@AA based on BHb was successfully synthesized by the surface grafting copolymerization method. The amounts of raw materials were optimized. The characteristics of the obtained MIP-Fe3O4@AA were determined by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The adsorption capacity of MIP-Fe3O4@AA was evaluated and well fitted by the Langmuir model. The maximum theoretical adsorption capacity (Qmax) was calculated to be 117.27 mg g−1 for MIP-Fe3O4@AA. The selectivity experiment showed that the MIP-Fe3O4@AA had an outstanding selectivity toward the template protein (BHb) with an imprinting factor of 4.43. The MIP-Fe3O4@AA was also used to capture BHb from the protein mixture and real sample with satisfactory results, which demonstrated its potential practical analytical performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...