Magnetic ELISA of aflatoxin B1 – pre-concentration without elution
Abstract
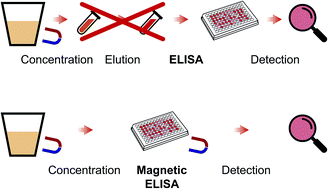
While immunoenzyme assay (ELISA) is widely used for the detection of various compounds, its use is significantly limited by the considerable duration (determined by the heterogeneous reaction to form detectable immune complexes) and the restricted detection limit. This study proposes an ELISA variant based on the application of highly dispersed (average diameter – 10 nm) magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as carriers for the adsorbable antibodies. In conducting the proposed ELISA, the antibodies react with the detectable compound within the sample volume; the formed complexes are preconcentrated by precipitation in a magnetic field and are used for immunoenzyme detection in the wells of a microplate. This approach has been implemented for the detection of aflatoxin B1, a low molecular weight compound that needs to be controlled at extremely low concentrations due to its high toxicity. Using magnetic nanoparticles provided a 10-fold lowering of the detection limit and cut the test duration by half, compared to conventional ELISA. Immobilized antibodies exhibited high resistance to methanol when testing aqueous/methanol extracts of contaminated vegetable feed stocks (corn kernels), making it possible to identify aflatoxin B1 at concentrations as low as 2 pg ml−1 (40 pg g−1). The proposed approach is universal and can be used for the immunodetection of various compounds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...