Comparative characterization of amino acids in Abelmoschus manihot roots, stems and leaves during different growth periods by UPLC-TQ-MS/MS†
Abstract
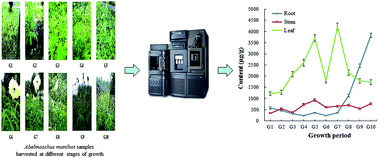
Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medicus is an annual herbal plant whose flowers, roots, stems and leaves possess pharmacological activities. However, due to the less information about types and contents of compounds such as amino acids contained in Abelmoschus manihot roots, stems and leaves, masses of them are discarded or burned after Abelmoschus manihot flowers are being picked for medicine. In our study, UPLC-TQ-MS/MS has been established for the simultaneous determination of amino acids in different parts harvested at ten growth periods. Under the optimized chromatographic conditions, good separation of 22 target compounds was achieved on an Acquity UPLC BEH Amide column within 19 min. The results revealed that the accumulation of amino acids in Abelmoschus manihot stems and leaves occurred mainly from G5 to G8, while their accumulation in the roots happened from G8 to G10, the deciduous periods of Abelmoschus manihot. Moreover, it turned out to be that γ-aminobutyric acid, glutamine, lysine, proline, asparagine and aspartic acid were the predominant types of total amino acids in all of the three parts. The data also showed that none of the samples contained hydroxyproline, and only the leaf samples had glycine and glutamate. The characterization of amino acids in Abelmoschus manihot roots, stems and leaves would be very helpful for their potential value improvements as food and medicine to provide amino acids, and also be beneficial to the choice of a suitable harvest time for different parts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...