Optimization of selective pressurized liquid extraction and ultrasonication-assisted QuEChERS methods for the determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments†
Abstract
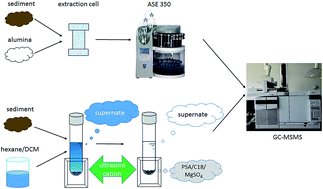
Two fast analytical methods, selective pressurized liquid extraction (SPLE) and ultrasonication-assisted QuEChERS methods (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged and Safe) followed by GC-MS/MS, were optimized for the determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediments. Ultrasonication was used to improve the extraction efficiency of QuEChERS. The experimental parameters of SPLE and ultrasonication-assisted QuEChERS, such as sorbent type, composition and elution solvents, were optimized in detail. The obtained recoveries of both methods were satisfactory for PBDE analysis. The inter/intra-day RSDs were <7%. The limits of quantification (LOQ) were ≤0.1 ng g−1 dry weight (d.w.). The figures of merit were at the same level as former reported results. The proposed methods were validated for the analysis of PBDEs in standard reference materials (SRM 1944 and 2585). The results indicated that both optimized methods were feasible for the analysis and monitoring of PBDEs. Besides, the comparison between two methods revealed that elevated temperature and pressure could weaken the interaction between PBDEs and sediment matrices, resulting in improvement of extraction efficiency. Both proposed methods were successfully applied to the analysis of 3 sediment samples and the determination of BDE 47, 99, 100 and 153 suggested that both methods are practical and suitable for PBDE analysis in real sediment samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...