Adsorption of cadmium(ii) and copper(ii) from soil and water samples onto a magnetic organozeolite modified with 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1,3-dithiane using an artificial neural network and analysed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry†
Abstract
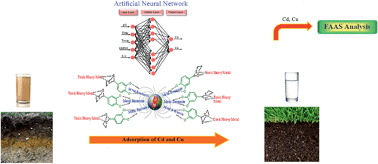
In this study an adsorbent, a magnetic zeolite modified with 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1,3-dithiane, was synthesized as an easily separable sorbent for the simultaneous removal of two toxic heavy metals, cadmium and copper, from soil and water samples. The synthesized magnetic sorbent was characterized by SEM and XRD. The magnetic properties of the sorbent were identified by the VSM method. The obtained saturation magnetization of 18.4 emu g−1 showed a facile separation of the magnetic modified zeolite after the adsorption process. The effects of the five dominant parameters of pH, temperature, time, amount of sorbent and sample solution volume on the adsorption process were investigated. The optimum conditions of 6, 25 °C, 9 min, 40 mg and 40 mL were acquired for pH, temperature, time, amount of sorbent and sample solution volume, respectively. Maximum experimentally achieved adsorption percentages of 98.2 ± 2.5 and 97.5 ± 2.8 were obtained under the optimum conditions which showed the high adsorption potential of the proposed sorbent. The experimental data were found to fit properly to the Langmuir and Freundlich models which indicated that the sorption took place on a heterogeneous material. Sorption capacities of 178.5711 and 181.8182 (mg g−1) were achieved for cadmium and copper respectively from sorption isotherms. A three-layer artificial neural network model with 8 neurons and a tan-sigmoidal function at the hidden layer and a linear transfer function (purelin) at the output layer was developed to predict the simultaneous removal of cadmium and copper. The results indicated that the proposed artificial neural network model could perfectly predict the process with a mean square error (MSE) of 0.037. The optimization procedure showed a close correlation between the experimental and predicted values.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...