Application of silver nanoparticles decorated with β-cyclodextrin in determination of 6-mercaptopurine by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Abstract
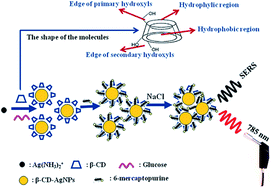
Although classical silver nanospheres were widely used as probes in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), they lacked long-term stability. In the present work, silver nanoparticles decorated with β-cyclodextrin (β-CD–AgNPs) were used as probes and the stability was improved. The adsorption characteristics of 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) on classical silver nanospheres and β-CD–AgNPs were studied cautiously using SERS, and chemical information about the molecular structure was obtained. The binding of the 6-MP molecule to the surface of AgNPs is based on the stable Ag–S covalent bond. The electrostatic adsorption between the protonated N7 atom or N1 atom and the silver surface results in a notable Raman enhancement. The intensity of the Raman band of 6-MP at 866 cm−1 was used to determine 6-MP. Experimental conditions, such as the volume of CD–AgNP solution, incubation time, pH value and concentration of sodium chloride, were examined and optimized. Compared with classical silver nanospheres, when β-CD–Ag nanoparticles were used, the sensitivity was higher, the analytical time was shorter, and the linear range was wider. A good linearity (r = 0.996) in the range of (0.040–2.0) × 10−7 mol L−1 was obtained for determining 6-MP. The limit of detection was 0.024 × 10−7 mol L−1 and the limit of quantification was 0.080 × 10−7 mol L−1. This method was successfully applied to the determination of 6-MP in real samples and the results were satisfactory.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...