Whole-cell based aptamer selection for selective capture of microorganisms using microfluidic devices†
Abstract
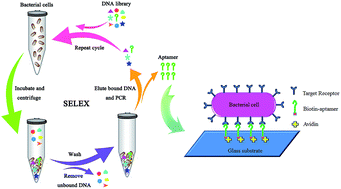
Selective capture of microorganisms is an effective and rapid technique for microbe detection. In this article, we obtained aptamers targeting live bacterial cells E. coli as recognition and capture elements by using a whole-cell based aptamer selection, and integrated the isolated aptamers into a microfluidic device for selective capture of microorganisms. Eight rounds of selection were performed; the specificity and affinity of aptamers to the target bacterial cells were also characterized using flow cytometric analysis. A total of 40 aptamer sequences were obtained, and the apparent dissociation constant Kd of the representative aptamer displaying the highest binding affinity was estimated to be 24.8 ± 2.7 nM. After sequencing of the pool showing the highest binding affinity to E. coli, a DNA sequence of high affinity to the bacteria was integrated into the microfluidic device as recognition and capture elements for selective capture of microorganisms. The results demonstrated that the aptamer-based microfluidic device was able to capture E. coli selectively to distinguish different species of bacteria. This investigation is envisaged to provide a new avenue for the development of lab-on-chip devices for selective capture of microorganisms, which could be beneficial for portable, rapid and economic microbial detection in food safety, environmental monitoring and medical diagnosis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Microfluidics Research 2015-2016

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...