A cation exchange based electrochemical sensor for cetyltrimethylammonium bromide detection using an acridine orange/polystyrene sulfonate system†
Abstract
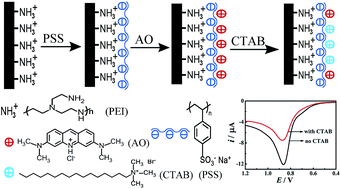
A simple and sensitive electrochemical method for the detection of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) by cation exchange processes has been developed. The rationale for the amperometric CTAB assay is essentially based on the different binding affinities of polystyrene sulfonate (PSS) toward electrochemically active acridine orange (AO) and electrochemically inactive CTAB. The stronger binding affinity of the PSS toward CTAB than toward AO essentially validates the amperometric CTAB assay through a cation exchange mechanism with the decrease in the redox peak current of AO adsorbed on the PSS. Because of the different binding affinities between PSS and cationic surfactants with different lengths of the alkyl chain, this method can be used to detect quaternary ammonium surfactants with similar structures. The difference value of the anodic peak current showed a linear relationship with the CTAB concentration in a concentration range from 0.5 to 20 μg mL−1 and a detection limit of 0.3 μg mL−1 was obtained. More importantly, this detection method has been successfully applied to the detection of CTAB in real samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...