A new calibration curve calculation method for absolute quantification of drug metabolizing enzymes in human liver microsomes by stable isotope dilution mass spectrometry†
Abstract
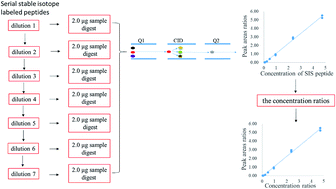
Accurate quantification of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes and uridine 5-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes is essential for the reliable assessment of the safety of new drugs and individual medicines. Stable isotope dilution-multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry (SID-MRM MS) has been used for the determination of drug metabolizing enzymes in complex biological samples, in which a working curve is often established by adding a series of light peptides into aliquots of a blank sample matrix and stable isotope-labeled (SIS) peptides. But when multiple proteins are simultaneously quantified, a blank sample matrix devoid of targeted proteins is difficult to prepare. To solve the problem, a linear curve was established by adding a series of SIS peptides to an actual sample instead of a heterologous or an artificial sample as a matrix, and a new calibration curve calculation method was proposed to calculate the concentrations of endogenous peptides or proteins in a biological sample as follows: a linear curve was first plotted with peak area ratios (SIS peptides/endogenous peptides) on the y-axis and the corresponding concentrations on the x-axis, and then the concentrations of endogenous peptides in a biological sample could be accurately obtained according to our mathematical formula. Finally, a working curve was built with peak area ratios on the y-axis and the corresponding concentration ratios on the x-axis, and when the peak area ratio of a transition of a peptide in a biological sample was measured and substituted into the working curve, the corresponding concentration ratio could be obtained to calculate the concentration of peptides. Experimental results demonstrated that the established method was reliable and sensitive with a recovery of 97.0%, the limit of quantification (LOQ) lower than 20 fmol, a linear range from 5 fmol, 10 fmol or 20 fmol–1000 fmol for different peptides and the coefficient of variation lower than 10%. The established method was applied to the determination of 21 drug metabolizing enzymes in five human liver microsomal samples, and the results are in agreement with the reported data, which proves that this method can be applied to the determination of targeted proteins in biological samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...