Correlation coefficient optimization in partial least-squares regression with application to ATR-FTIR spectroscopic analysis
Abstract
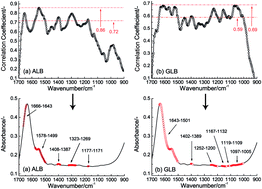
A wavelength selection method for spectroscopic analysis, named correlation coefficient optimization coupled with partial least-squares (CCO-PLS), is proposed, and was successfully employed for reagent-free ATR-FTIR spectroscopic analysis of albumin (ALB) and globulin (GLB) in human serum. By varying the upper bound of correlation coefficient between absorbance and analyte's content, the CCO-PLS method achieved multi-band selection. Two PLS-based methods, which used a waveband having positive peaks of the first loading vector (FLV) and a combination of positive peaks of the correlation coefficient spectrum, were also conducted for comparison. Based on the leave-one-out cross-validation for CCO-PLS, appropriate waveband combinations for ALB and GLB were selected, the root-mean-square errors of prediction for validation samples were 1.36 and 1.35 (g L−1) for ALB and GLB, respectively, which were better than the two comparison methods. The CCO-PLS method provided a new approach for multi-band selection to achieve high analytical accuracy for molecular absorption bands that were composed of several spaced wavebands.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...