Electrical conductivity, isothermal stability and amine sensing studies of a synthetic poly-o-toluidine/multiwalled carbon nanotube/Sn(iv) tungstate composite ion exchanger doped with p-toluene sulfonic acid
Abstract
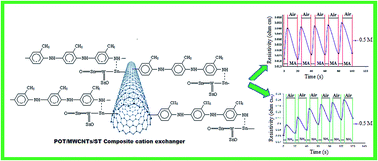
An electrically conductive poly-o-toluidine (POT) composite doped with p-toluene sulfonic acid (pTSA) was prepared using multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and Sn(IV) tungstate (ST) by in situ oxidative polymerization. The pTSA-doped POT, POT/MWCNT and POT/MWCNT/ST composites were characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, UV-visible spectrometry and thermogravimetric analysis. The thermogravimetric analysis studies showed that the POT/MWCNT/ST composite was thermally more stable than the pure polymer and the POT/MWCNT composite. The electrical conductivity behaviour of the POT/MWCNT composite was better than that of pure POT and the POT/MWCNT/ST composite. Ammonia and amine vapour sensing studies of the POT/MWCNT/ST composite ion exchangers showed an improved performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...