Screening and structural characterization of potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from Radix Astragali flavonoids extract by ultrafiltration LC-DAD-ESI-MSn
Abstract
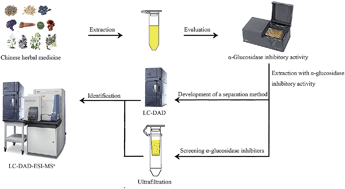
Inhibition of intestinal α-glucosidase activity is one important mechanism for the management of diabetes mellitus (DM). Identifying plants with α-glucosidase inhibitory activities and screening active compounds (α-glucosidase inhibitors) in them has become a popular field of research in the treatment of DM. In the present study, we used an in vitro assay of ultraviolet spectrophotometry to evaluate the α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of Radix Astragali flavonoids extract (RAFE). Then, ultrafiltration liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (ultrafiltration LC-DAD-ESI-MSn) was used to screen the active compounds in RAFE. As a result, the concentration (final) of RAFE required for 50% enzyme inhibition (IC50) was calculated as 2.888 mg mL−1. Through ultrafiltration LC-DAD-ESI-MSn analysis, seven compounds were identified as potential active compounds. They were calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside, biochanin A, calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside-6′′-O-malonate, ononin, calycosin, formononetin-7-O-β-D-glucoside-6′′-O-malonate and formononetin. Then, two of the potential active compounds, biochanin A and formononetin, were evaluated for α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Their IC50 values were calculated as 0.020 mM and 0.027 mM respectively, while that of the reference drug acarbose was calculated as 0.382 mM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...