An electrochemical and computational study for discrimination of d- and l-cystine by reduced graphene oxide/β-cyclodextrin
Abstract
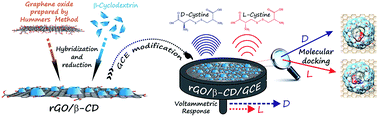
Here, we report a novel enantioselective electrochemical biosensor for the discrimination of cystine enantiomers (D- and L-cystine) using a chiral interface for the specific recognition of D- and L-cystine. The biosensor is based on reduced graphene oxide modified by β-cyclodextrin (rGO/β-CD) at the GCE surface. During the preparation of rGO/β-CD/GCE, the modified electrode surfaces were characterized by cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The electrochemical behaviours of the D- and L-cystine were investigated using the rGO/β-CD/GCE by CV and compared to bare GCE. A clear separation between the oxidation peak potentials of D- and L-cystine was observed at 1.32 and 1.42 V, respectively. The electrochemical discrimination performance of the fabricated chiral sensor was also examined by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) in a mixed solution of D- and L-cystine. In addition, the DPV technique was used for the determination of D- and L-cystine at low concentration values in the range of 1.0–10.0 μM. To investigate the amperometric response of rGO/β-CD/GCE towards D- and L-cystine, the chronoamperometry technique was used in the concentration range of 10.0–100.0 μM. The interactions of the enantiomers with rGO/β-CD were modelled by molecular docking using AutoDock Vina, and the interaction energies were predicted to be −4.8 and −5.3 kcal mol−1 for D- and L-cystine, respectively. The corresponding values of binding constants were calculated to be 3.32 × 103 and 7.71 × 103 M−1, respectively. The experimental and molecular docking results indicate that the rGO/β-CD/GCE has a different affinity for each enantiomer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...