A microfluidic interface for the culture and sampling of adiponectin from primary adipocytes
Abstract
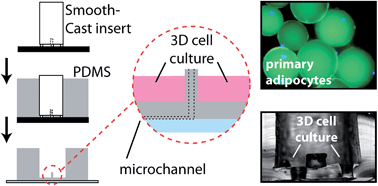
Secreted from adipose tissue, adiponectin is a vital endocrine hormone that acts in glucose metabolism, thereby establishing its crucial role in diabetes, obesity, and other metabolic disease states. Insulin exposure to primary adipocytes cultured in static conditions has been shown to stimulate adiponectin secretion. However, conventional, static methodology for culturing and stimulating adipocytes falls short of truly mimicking physiological environments. Along with decreases in experimental costs and sample volume, and increased temporal resolution, microfluidic platforms permit small-volume flowing cell culture systems, which more accurately represent the constant flow conditions through vasculature in vivo. Here, we have integrated a customized primary tissue culture reservoir into a passively operated microfluidic device made of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Fabrication of the reservoir was accomplished through unique PDMS “landscaping” above sampling channels, with a design strategy targeted to primary adipocytes to overcome issues of positive cell buoyancy. This reservoir allowed three-dimensional culture of primary murine adipocytes, accurate control over stimulants via constant perfusion, and sampling of adipokine secretion during various treatments. As the first report of primary adipocyte culture and sampling within microfluidic systems, this work sets the stage for future studies in adipokine secretion dynamics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...