Direct analysis of in-gel proteins by carbon nanotubes-modified paper spray ambient mass spectrometry†
Abstract
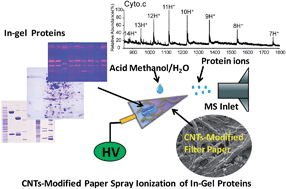
The in situ and direct extraction, desorption and ionization of in-gel intact proteins after electrophoresis has been achieved by carbon nanotubes (CNTs)-modified paper spray mass spectrometry at ambient conditions. Characteristics of CNTs (including larger surface area, smaller pore diameter and enhanced conductivity) were endowed to the porous filter paper substrate by uniformly dispersing the CNTs on the filter paper. Upon applying electric potential to the CNTs-modified paper, the in-gel proteins were extracted from the gel and subsequently migrated to the tip of the filter paper by electrophoresis-like behavior for paper spray ionization, which was monitored by extracted ion chronograms. The characterizations of modified filter papers and CNTs nanoparticles further confirmed the role of CNTs in in-gel protein extraction, protein migration as well as spray ionization at the paper tip. Under optimized conditions, a mixture of cytochrome c, lysozyme and myoglobin was successfully separated by native electrophoresis and subsequently analysed by the present method, showing a limit of detection of 10 ng per gel band. The present strategy offers a new pathway for the direct detection of in-gel intact proteins at ambient conditions without any pre-treatment (e.g. digestion, chemical extraction and desalting), which exhibits potential applications in top-down proteomics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...