Miniaturisation and simplification of solid-state proton activity sensors for non-aqueous media and ionic liquids†
Abstract
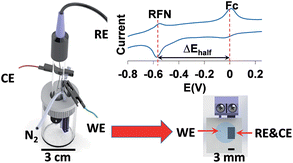
This work is the further development of the previous pH (effective) sensor work where a biologically derived proton-active redox centre – riboflavin (RFN) – was entrapped into a vapour phase polymerised poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) film and ferrocene (Fc) dissolved in the sample solution was used as an internal reference redox couple. Here, we report a disposable solid state pH (effective) sensor where we successfully incorporated both RFN and Fc into a single solid state electrode. The electrodes were then used for pH (effective) sensing where water is not required. The system was further miniaturised and simplified from a 3 electrode to a 2 electrode setup with the working electrode area being as small as 0.09 mm2. The sensors show the ability to measure pH (effective) in both aqueous and non-aqueous media including ionic liquids (ILs) regardless of their hydrophobicity. This is an important step towards the ability to customise ILs or non-aqueous media with suitable proton activity (PA) for various applications e.g. customised ILs for biotechnological applications such as protein preservation and customised media for PA dependent reactions such as catalytic reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...