Carbon dot reduced bimetallic nanoparticles: size and surface plasmon resonance tunability for enhanced catalytic applications†
Abstract
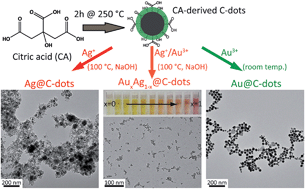
We report on a simple and green route toward monometallic (Au or Ag) and alloyed bimetallic AuAg nanoparticles using citric acid-derived carbon nanodots (C-dots) as the reducing and stabilizing agent. Simple variation in the initial C-dot : metal ratio yields a smoothly tunable surface plasmon resonance and the resulting nanomaterials show excellent catalytic activity for 4-nitrophenol reduction which is fully preserved following 5 months of storage. The Au@C-dot catalyst further demonstrated intrinsic peroxidase activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...