New insights into self-modification of mesoporous titania nanoparticles for enhanced photoactivity: effect of microwave power density on formation of oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ defects†
Abstract
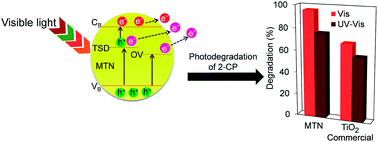
Mesoporous titania nanoparticles (MTN) were successfully prepared by a microwave (MW)-assisted method under various power densities. The catalysts were characterized by XRD, FT-IR, surface area analysis, TEM, and ESR. The characterization data indicated that higher power density increased the crystallinity and surface area of the MTN while decreasing the particle size and band-gap energy of the TiO2. Significantly, MW heating played an important role in formation of oxygen vacancies (OV) and Ti3+ site defects (TSD). The MTN (T1–T3) with 0.12, 0.37, and 0.56 W g−1 power density were found to degrade 84%, 88%, and 96% of 2-chlorophenol (2-CP) under visible light, respectively, compared to 69% by commercial TiO2. Besides narrowing the band gap, the OV and TSD also acted as electron acceptors that hindered the electron–hole recombination, as well as facilitated the charge carrier migration. The kinetics study over T3 showed that adsorption was the controlling step in the 2-CP degradation, which followed a pseudo-first-order Langmuir–Hinshelwood model. The photocatalytic reaction was still stable, even after five cycle runs without severe catalyst deactivation. This study demonstrates that the uniform heat distribution provided by MW is able to produce MTN that are rich with OV and TSD that are effective under visible light irradiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...