Antimicrobial and sustainable food packaging based on poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and electrospun chitosan nanofibers
Abstract
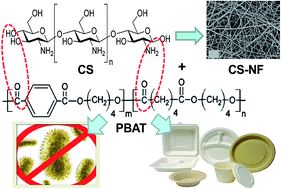
Antimicrobial packaging systems are developed to increase the shelf life of foods by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms. In this work, antimicrobial poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) films incorporating different amounts of chitosan nanofibers (CS-NF) have been prepared via solution casting technique. Their morphology, structure, thermal stability, crystallization and melting behaviour, water absorption, hydrophilicity, barrier, migration, antibacterial, mechanical and viscoelastic properties have been investigated. Uniform films without pores were attained, as revealed by SEM, suggesting good compatibility between the matrix and nanofiller phases. Further, IR spectra demonstrated the existence of strong H-bonding interactions between PBAT and CS-NF. The nanofibers acted as nucleating agents, raising the crystallization temperature and the degree of crystallinity of the copolyester, and also increased its thermal stability and flammability. Compared to neat PBAT, the biocomposites showed higher stiffness, strength and glass transition temperatures whilst reduced ductility, oxygen and water vapour permeability. For all the nanocomposites, the migration levels in both non-polar and polar simulants were considerably below the overall limits established by the current legislation on food contact materials. The films displayed antibacterial activity against common foodborne pathogens: Gram-positive S. aureus and B. subtilis as well as Gram negative S. enteritidis and E. coli bacteria, and the biocide effect was systematically stronger against Gram-negative cells. These sustainable and biodegradable antimicrobial films meet the growing demand for green packaging from the food and beverage industry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...