Organic dyes for the sensitization of nanostructured ZnO photoanodes: effect of the anchoring functions†
Abstract
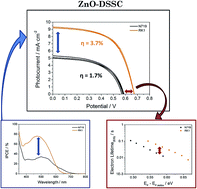
Among all n-type metal oxide semiconductors that can be used in solar cells as photoanode, ZnO is one of the most appealing alternatives to the ubiquitous TiO2. This material offers some potentially favourable characteristics with respect to TiO2, such as higher electron mobility in the bulk and a rich variety of nanostructures. However, ZnO has certain drawbacks as photoanode material, for example, a poor chemical stability and a slower charge separation process at the ZnO interface that reduces the electron injection rate. Therefore, in the case of dye-sensitized solar cells, the search of new dyes with a higher light harvesting efficiency and specifically designed to bind to ZnO can be considered as a possible strategy to improve performance in systems characterized by a low electron injection rate. In this work the optical, electrochemical and photovoltaic properties of a family of purely organic sensitizers with various anchoring groups have been investigated and compared with the most commonly used ruthenium dye N719. In particular, we have shown that the structurally simple organic dye coded RK1 is an excellent sensitizer for ZnO photoanodes. Thanks to this molecule, the energy conversion efficiency under standard conditions (1 sun AM 1.5 illumination) employing ZnO-based photoanodes reached 3.7%, which is more than two times higher than obtained with the N719 dye studied under the same conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...