In situ synthesis of permselective zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/graphene oxide composites: rotating disk electrode and Langmuir adsorption isotherm†
Abstract
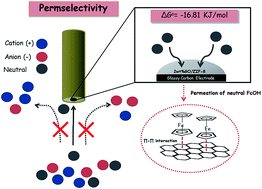
Although zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) has been well known and widely used in gas storage and catalysis applications, its electrochemical application has not yet been well investigated due to its poor conductivity limiting the electronic charge transfer. In this work, graphene oxide (GO) has been loaded to ZIF-8 using an in situ synthesis in order to improve its conductivity. The morphological, structural and electrochemical properties of GO/ZIF-8 composites were studied by scanning electron and transmission electron microscopies, X-ray photoelectron and absorption spectroscopies, voltammetry, rotating disk electrode, and Langmuir adsorption isotherm. It was found that a 2 wt% loading content of GO to ZIF-8 shows high permselective property to redox probe mediators enhancing the Faradaic current of ferrocene methanol (FcOH) but reducing the Faradaic current of Fe(CN)64−. Gibbs's free energy (ΔG0) of the adsorption of FcOH within the 2 wt%GO/ZIF-8 film is −16.81 kJ mol−1 indicating the spontaneous adsorption process. This composite may lead to many useful electrochemical applications of ZIF-8 especially in a research area of the permselective membrane.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...