Identifying MurI uncompetitive inhibitors by correlating decomposed binding energies with bioactivity†‡
Abstract
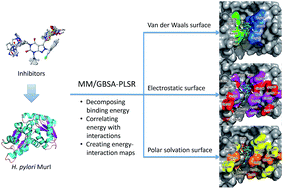
The glutamate racemase (MurI) is essential for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) cell wall biosynthesis. In this work, we report a new method that correlates decomposed binding free energies with MurI inhibition based upon the data from pyrazolopyrimidinedione series MurI uncompetitive inhibitors. With the molecular mechanics/generalized Born surface areas (MM/GBSA) approach, we were able to decompose the binding interaction into van der Waals, electrostatic, and polar solvation surfaces. The decomposed binding energies were correlated with MurI inhibitory activity with partial least squares regression (PLSR). Hence, the method is termed MM/GBSA-PLSR. The non-cross-validation (R2) and leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV) (Q2) correlation coefficients of the 3D-QSAR model are 0.962 and 0.822, respectively. The external testing yields a predicted correlation coefficient (Rpred2) of 0.817. This study demonstrated that the activity-contribution fractions from the three types of ligand–receptor interactions are 29.5% from van der Waal interactions, 38.2% from electrostatic interactions, and 32.3% from polar solvation interactions. Comparing with molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity index analysis (CoMSIA), we find that the CoMFA/CoMSIA steric interaction fields can be interpreted as the MM/GBSA-PLSR van der Waals interactions; CoMFA/CoMSIA electrostatic and H-bond acceptor/donor interaction fields can be interpreted as the MM/GBSA-PLSR electrostatic interactions. However, there is no explicit association between MM/GBSA-PLSR solvation interactions (polar or non-polar) and CoMFA/CoMSIA fields. It is worth noting that the solvation interaction is important for ligand design. Moreover, MM/GBSA-PLSR maps the decomposed binding interactions on to pharmacophore surfaces (van der Waals, electrostatic, and polar solvation surfaces) to aid drug design.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...