pH/redox dual-sensitive nanoparticles based on the PCL/PEG triblock copolymer for enhanced intracellular doxorubicin release†
Abstract
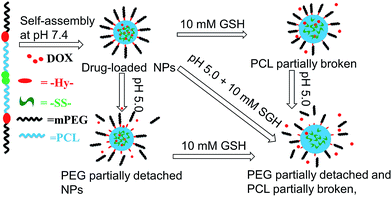
pH/redox dual-sensitive nanoparticles (NPs) based on a poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and polyethylene glycol (PEG) triblock copolymer were developed and investigated aiming at improving the drug release property of PCL in cancer chemotherapy. A redox-sensitive disulfide bond and pH-sensitive benzoic-imine linkers were introduced to the backbone of the amphiphilic block copolymer termed SCHE, which could self-assemble into stable spherical NPs in aqueous solutions with an average size of about 100 nm. Doxorubicin (DOX) as a hydrophobic anticancer drug was loaded into the NPs by a dialysis method. The in vitro drug release results showed that the accumulative release amount of DOX at pH 5.0 with 10 mM glutathione (GSH) was accelerated apparently by more than twice compared to that at pH 7.4 without GSH. After a pre-treatment with GSH, the intracellular fluorescence intensity of Hela cells was enhanced compared to those without the pretreatment, which indicated faster DOX release in cells with higher GSH concentration. In an MTT assay, no obvious toxicity of blank NPs was found. In conclusion, SCHE NPs could serve as a novel colloidal drug delivery system in cancer chemotherapy and the introduced unstable linkers could enhance the drug release rate at tumor sites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...