Amino-functionalized magnetic magnesium silicate double-shelled hollow microspheres for enhanced removal of lead ions†
Abstract
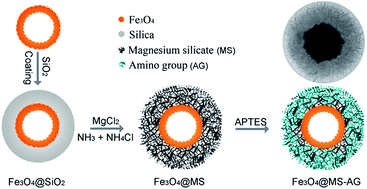
Magnesium silicate hollow microspheres with porous structure were synthesized using silica microspheres as chemical template, which exhibited excellent adsorption properties to heavy metal ions in water in our previous report. Herein, both an iron magnetic core and amino-groups were put forward to functionalize the magnesium silicate hollow microspheres for a fast recoverable and highly efficient absorbent. In the synthesis process, double-shelled hollow microspheres with iron oxide (Fe3O4) inner shell and magnesium silicate outer shell (DS-Fe3O4/MS) were realized via hydrothermal treatment of Fe3O4@SiO2 double-shelled hollow microspheres in ammonia solution containing magnesium ions, and the amino-group was introduced into the porous surface of the magnesium silicate shell by a refluxing method to increase the active adsorption sites. The experimental results show that the amino-functionalized magnetic magnesium silicate double-shelled hollow microspheres (DS-Fe3O4/MS-AG) exhibited a high adsorption capacity of 315.5 mg g−1, and the high adsorption capacity was proposed to be due to synergic adsorption from the magnesium silicate shell (ion-exchange adsorption), surface-modified amino-groups (complexation adsorption) and the carboxyl groups on the inner iron oxide hollow microspheres (electrostatic adsorption). Additionally, the used DS-Fe3O4/MS-AG hollow microspheres could be easily regenerated through immersing them in a solution containing magnesium ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...