Enhanced water retention and proton conductivity of proton exchange membranes by incorporating hollow polymer microspheres grafted with sulfonated polystyrene brushes†
Abstract
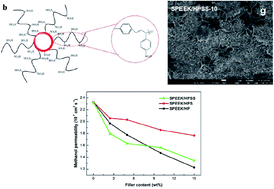
Hollow polymer microspheres grafted with sulfonated polystyrene brushes (HPSS) were synthesized via a combination of surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ATRP) of styrene from SiO2@P(MAA-co-DVB-co-CMSt) core–shell microspheres, sulfonation of the polystyrene brushes, and final removal of the silica core. These HPSSs were then incorporated into a sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK) matrix to fabricate hybrid membranes. As a comparison, SPEEK/HPS hybrid membranes were prepared by incorporation of sulfonated hollow polymer microspheres (HPS) into a SPEEK matrix. Water retention, methanol resistance and proton conductivity were increased by doping with both kinds of hollow polymer microspheres. The SPEEK/HPSS hybrid membranes exhibited much higher proton conductivity than did the SPEEK/HPS hybrid membranes with the same filler contents ranging from 2.5 to 15 wt%. The highest conductivity was obtained at 0.33 S cm−1 for SPEEK/HPSS under 75 °C and 100% relative humidity (RH), which was 83.3% higher than that (0.18 S cm−1) for a SPEEK control membrane under the same conditions. The increment in proton conductivity was mainly attributed to the large cavities of HPSS acting as water reservoirs, and the excellent flexibility and high accessibility of the sulfate groups (–SO3H) on the surface grafted polymer brushes, which provide proton hopping sites for proton-conducting pathways. Moreover, the hybrid membranes exhibited good thermal and mechanical stability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...