Catalytic oxidation of cinnamyl alcohol using Au–Ag nanotubes investigated by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy†
Abstract
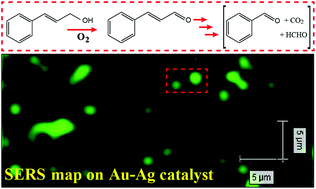
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) enables ultrasensitive detection of adsorbed species at the catalyst surface. However, it is quite difficult to combine catalytic and SERS activities on the same material. Here we report the application of well-defined Au–Ag nanotubes as both SERS substrates and catalysts for the oxidation of cinnamyl alcohol. The species adsorbed on the catalyst surfaces at different reaction times were analyzed by SERS. The bimetallic nanotubes prepared via a simple galvanic replacement reaction are highly active in the oxidation of cinnamyl alcohol, but do not avoid a radical-chain reaction and the cleavage of the carbon–carbon double bond. A comparison between changes in bulk composition and the nature of adsorbed species at the surface of the catalyst over time suggests that cinnamaldehyde is formed on the catalyst surface (metal-catalyzed oxidation) and benzaldehyde is probably formed in the bulk solution via a radical-chain pathway. In the presence of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, the radical-chain reaction is suppressed and the oxidation reaction produces cinnamaldehyde.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...