The design of phenylboronic acid azoprobe–polyamidoamine dendrimer complexes as supramolecular sensors for saccharide recognition in water†
Abstract
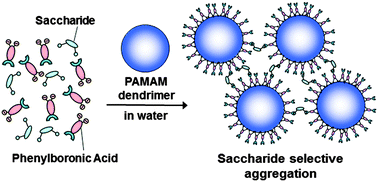
The selective molecular recognition event by physical or chemical signals is a key concept for the design of novel supramolecular sensors. In this study, we designed a novel saccharide recognition system based on the self-assembly of phenylboronic acid azoprobes (1-BAzo-NPs) on the surface of the polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimer in water. The two sulfonic acid moieties in 1-BAzo-NP enhanced the binding affinity of the azoprobe for the PAMAM dendrimer surface. UV-Vis spectral measurements indicated that 1-BAzo-NP showed poor saccharide recognition at pH 7.0, whereas the 1-BAzo-NP–PAMAM complex well recognized the saccharides, particularly glucose. The complexation with glucose yielded aggregates having diameters of 100–200 nm as determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The sensitivity to and selectivity for the saccharides were controlled by the density of the assembled phenylboronic acid azoprobes and PAMAM generation. Together, the results revealed that the selective saccharide recognition at pH 7.0 was feasible by boronic acid assembly on the PAMAM dendrimer surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...