Effect of vitamin E succinate on the expression of the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor in gastric cancer cells and CD4+ T cells
Abstract
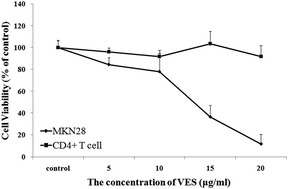
Gastric malignancy, which shows poor prognosis, is one of the most frequent causes of cancer-associated deaths. Vitamin E succinate (VES) inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. We explored the effect of VES on the expression of the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor in gastric cancer cells and CD4+ T cells. On one hand, VES dose-dependently regulated the expression of the TRAIL receptor in gastric cancer cells. Moreover, the activation of the TRAIL receptor, death receptor 4 (DR4), and death receptor 5 (DR5) in gastric cancer cells increased for up to 12 h. On the other hand, the expression of TRAIL protein in human CD4+ T cells was obviously upregulated in the presence of VES. On the basis of these findings, we combined VES and human CD4+ T cells to induce apoptosis of MKN28 human gastric cancer cells. The results showed that VES induced higher gastric cancer cell apoptosis when combined with human CD4+ T cells than when applied alone. We conclude that VES can induce the expression of TRAIL receptor in gastric cancer cells, as well as the expression of TRAIL in CD4+ T cells. Overall, our results provide a theoretical basis for future immunotherapy studies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...