A microfluidic device and automatic counting system for the study of C. elegans reproductive aging†
Abstract
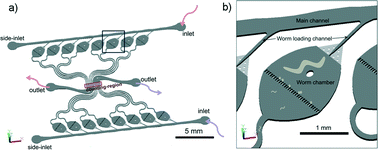
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is an excellent model to study reproductive aging because of its short life span, its cessation of reproduction in mid-adulthood, and the strong conservation of pathways that regulate longevity. During its lifetime, a wild-type C. elegans hermaphrodite usually lays about 200–300 self-fertilized hatchable eggs, which mainly occurs in the first three to five days of adulthood. Here, we report the development of a microfluidic assay and a real-time, automatic progeny counting system that records progeny counting information from many individual C. elegans hermaphrodites. This system offers many advantages compared to conventional plate assays. The flow of non-proliferating bacteria not only feeds the worms but also flushes the just-hatched young progeny through a filter that separates mothers from their offspring. The progeny that are flushed out of the chamber are detected and recorded using a novel algorithm. In our current design, one device contains as many as 16 individual chambers. Here we show examples of real-time progeny production information from wild-type (N2) and daf-2 (insulin receptor) mutants. We believe that this system has the potential to become a powerful, high time-resolution tool to study the detailed reproduction of C. elegans.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...