Towards lignin consolidated bioprocessing: simultaneous lignin depolymerization and product generation by bacteria†
Abstract
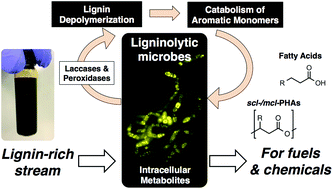
Lignin represents an untapped resource in lignocellulosic biomass, primarily due to its recalcitrance to depolymerization and its intrinsic heterogeneity. In Nature, microorganisms have evolved mechanisms to both depolymerize lignin using extracellular oxidative enzymes and to uptake the aromatic species generated during depolymerization for carbon and energy sources. The ability of microbes to conduct both of these processes simultaneously could enable a Consolidated Bioprocessing concept to be applied to lignin, similar to what is done today with polysaccharide conversion to ethanol via ethanologenic, cellulolytic microbes. To that end, here we examine the ability of 14 bacteria to secrete ligninolytic enzymes, depolymerize lignin, uptake aromatic and other compounds present in a biomass-derived, lignin-enriched stream, and, under nitrogen-limiting conditions, accumulate intracellular carbon storage compounds that can be used as fuel, chemical, or material precursors. In shake flask conditions using a substrate produced during alkaline pretreatment, we demonstrate that up to nearly 30% of the initial lignin can be depolymerized and catabolized by a subset of bacteria. In particular, Amycolatopsis sp., two Pseudomonas putida strains, Acinetobacter ADP1, and Rhodococcus jostii are able to depolymerize high molecular weight lignin species and catabolize a significant portion of the low molecular weight aromatics, thus representing good starting hosts for metabolic engineering. This study also provides a comprehensive set of experimental tools to simultaneously study lignin depolymerization and aromatic catabolism in bacteria, and provides a foundation towards the concept of Lignin Consolidated Bioprocessing, which may eventually be an important route for biological lignin valorization.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Lignin chemistry and valorisation

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...