Influence of milk fermented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCDC 17 alone and in combination with herbal ingredients on diet induced adiposity and related gene expression in C57BL/6J mice
Abstract
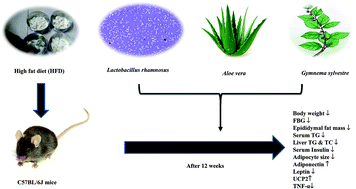
Obesity has become a major health problem in developed countries and is rapidly catching up in the developing world due to changes in their life style. Dietary incorporation of functional foods, including probiotic fermented milk and herbal ingredients, is being tried to ameliorate metabolic disorders. In the present study, the effect of dietary supplementation of a probiotic (Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCDC 17) fermented milk alone or either of the herbal preparations (Aloe vera/Gymnema sylvestre powders, 1% w/w) on the progression of obesity has been studied in C57BL/6J mice fed with a high fat diet for 12 weeks. At the end of the experimental period, oral administration of L. rhamnosus and herbs resulted in a significant decrease in the body weight, epididymal fat mass, fasting blood glucose and serum insulin levels. Supplementation of the probiotic L. rhamnosus alone and in combination with herbs showed a significant decrease in the adipocyte cell size and an increase in the number. Finally, obesity related adipokines levels were maintained at normal by the treatment groups. Thus, dietary intervention of milk fermented with probiotic L. rhamnosus alone or in combination with any of the herbal preparations seems to show anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...