BSA-directed synthesis of CuS nanoparticles as a biocompatible photothermal agent for tumor ablation in vivo†
Abstract
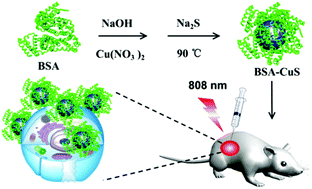
Photothermal therapy as a physical therapeutic approach has greatly attracted research interest due to its negligible systemic effects. Among the various photothermal agents, CuS nanoparticles have been widely used due to their easy preparation, low cost, high stability and strong absorption in the NIR region. However, the ambiguous biotoxicity of CuS nanoparticles limited their bio-application. So it is highly desirable to develop biocompatible CuS photothermal agents with the potential of clinical translation. Herein, we report a novel method to synthesize biocompatible CuS nanoparticles for photothermal therapy using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a template via mimicking biomaterialization processes. Owing to the inherent biocompatibility of BSA, the toxicity assays in vitro and in vivo showed that BSA–CuS nanoparticles possessed good biocompatibility. In vitro and in vivo photothermal therapies were performed and good results were obtained. The bulk of the HeLa cells treated with BSA–CuS nanoparticles under laser irradiation (808 nm) were killed, and the tumor tissues of mice were also successfully eliminated without causing any obvious systemic damage. In summary, a novel strategy for the synthesis of CuS nanoparticles was developed using BSA as the template, and the excellent biocompatibility and efficient photothermal therapy effects of BSA–CuS nanoparticles show great potential as an ideal photothermal agent for cancer treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...