Monooxygenation of an appended phenol in a model system of tyrosinase: implications on the enzymatic reaction mechanism†
Abstract
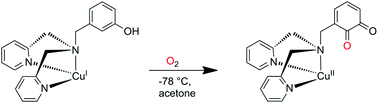
A new tridentate N-donor ligand and its corresponding copper(I) complex have been synthesized to investigate the tyrosinase-like aromatic hydroxylation of an attached phenol. The results of the oxygenation reactions are compared to related systems having attached phenyl and catechol groups, respectively. The title complex is the first system mediating the monooxygenation of a phenol in the absence of an external base.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...