Evolution of water sorption in catalyst coated membranes subjected to combined chemical and mechanical degradation
Abstract
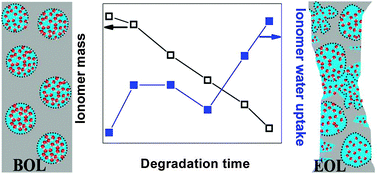
Catalyst coated perfluorosulfonic acid ionomer membranes (CCMs) were subjected to a combined chemical/mechanical accelerated stress test (AST) designed for rapid benchmarking of in situ membrane stability in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. In order to understand the evolution of the ionomer water sorption characteristics during combined chemical/mechanical degradation, CCM samples were periodically extracted from the AST and analyzed for ionomer mass fraction and water sorption properties. In spite of severe fluoride release and membrane thinning, the water uptake per unit mass of the partially degraded CCMs was found to be essentially constant. The mass fraction of ionomer in the CCM samples determined from thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) showed significant material loss throughout the AST process due to ionomer degradation and fluoride release, up to roughly 50% at end-of-life. The effects proceeding at different stages of degradation were therefore more accurately revealed by ionomer mass-normalized data. The water uptake per unit gram of ionomer was shown to increase significantly with degradation, in contrast to the previous results normalized by CCM dry mass. Although increased water sorption may indicate enlarged solvated hydrophilic domains in the membrane, which would be beneficial for enhanced proton mobility, the proton conductivity was found to decrease. This finding suggests that the additional water sorbed in the membrane was not contributing to proton conduction and was therefore likely situated in non-ionic cavities formed through degradation rather than in the ionic clusters.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...