Correlating structure with non-linear optical properties in xAs40Se60·(1 − x)As40S60 glasses
Abstract
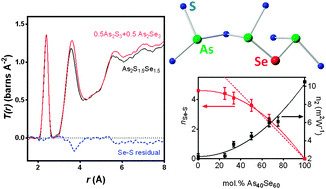
A series of xAs40Se60·(100 − x)As40S60 glasses, where x = 0, 25, 33, 50, 67, 75 and 100 mol% As40Se60, has been studied using neutron and X-ray total scattering, Raman spectroscopy and 77Se MAS-NMR. The results are presented with measurements of non-linear refractive indices, n2, and densities. There is no evidence for the formation of homopolar bonds in these glasses, but neutron correlation functions suggest that there is a non-random distribution of sulfur and selenium atoms in sulfur-rich glasses. The average number of sulfur atoms at a distance of 3–4 Å from a selenium atom, nSeS, deviates from a linear variation with x in glasses containing <50 mol% As40Se60; n2 for these glasses also varies non-linearly with x. Importantly, a direct comparison of n2 and nSeS gives a linear correlation, suggesting that n2 may be related to the distribution of chalcogen atoms in the glasses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...