Magnetic γ-Fe2O3, Fe3O4, and Fe nanoparticles confined within ordered mesoporous carbons as efficient microwave absorbers†
Abstract
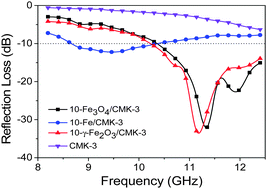
A series of magnetic γ-Fe2O3, Fe3O4, and Fe nanoparticles have been successfully introduced into the mesochannels of ordered mesoporous carbons by the combination of the impregnation of iron salt precursors and then in situ hydrolysis, pyrolysis and reduction processes. The magnetic nanoparticles are uniformly dispersed and confined within the mesopores of mesoporous carbons. Although the as-prepared magnetic mesoporous carbon composites have high contents of magnetic components, they still possess very high specific surface areas and pore volumes. The magnetic hysteresis loops measurements indicate that the magnetic constituents are poorly-crystalline nanoparticles and their saturation magnetization is evidently smaller than bulky magnetic materials. The confinement of magnetic nanoparticles within the mesopores of mesoporous carbons results in the decrease of the complex permittivity and the increase of the complex permeability of the magnetic nanocomposites. The maximum reflection loss (RL) values of −32 dB at 11.3 GHz and a broad absorption band (over 2 GHz) with RL values <−10 dB are obtained for 10-Fe3O4–CMK-3 and 10-γ-Fe2O3–CMK-3 composites in a frequency range of 8.2–12.4 GHz (X-band), showing their great potentials in microwave absorption. This research opens a new method and idea for developing novel magnetic mesoporous carbon composites as high-performance microwave absorbing materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...