Formation of double layer hollow nanostars of Pd/CuIr by utilizing a Kirkendall effect and a facile Cu atom movement along twinning boundaries and their usage as efficient water splitting catalysts†
Abstract
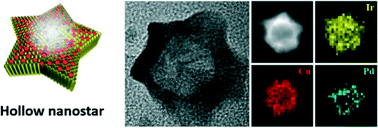
Hollow nanostructures with an inherent high surface area per mass are attractive candidates as economically viable catalysts. Conceptually, a hollow nanostructure can be obtained by forming a desired material phase on a removable template and then by subsequently removing the template core. We recently reported the synthesis of a core–shell type structure with a Cu-rich core and Ir rich shell. However, the Cu phase could not be removed from the core due to the imperviousness of the single crystalline Ir-rich shell. In order to facilitate the Cu phase removal, we introduced the polycrystalline Pd seed into the growth of the CuIr nanocrystal, which resulted in the formation of Pd@CuIr nanocrystals with multiple radial grain boundaries. By placing the Pd@CuIr nanocrystal under oxidizing conditions, we could initiate the outward movement of the Cu phase along the grain boundaries. Herein we report the synthesis of an unusual bilayer hollow nanostructure with a CuIr surface layer and a Pd inner-coating layer, following a facile CuPd alloy phase formation and an outward movement of the Cu phase under oxidizing conditions. We also report the high catalytic performance of the hollow nanostructure in oxygen evolution reaction (OER).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...