Study on the chemical markers of Caulis Lonicerae japonicae for quality control by HPLC-QTOF/MS/MS and chromatographic fingerprints combined with chemometrics methods
Abstract
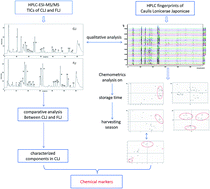
Caulis Lonicerae japonicae (CLJ), one of the commonly used herb drugs in Chinese Pharmacopoeia, has been used in China for centuries. A simple and reliable high-performance liquid chromotography (HPLC) fingerprint combined with a chemometrics method was developed to measure CLJ quality. Thirty-six batches of CLJ samples that varied by crop location, time in storage, and harvest season. Differences in chemical composition between CLJ and Flos Lonicerae japonicae (FLJ) were analyzed via high-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS). A total of 42 major constituents were screened and identified, and the fragmentation patterns of some iridoid glycosides, such as L-phenylalaninosecologanin and grandifloroside, were explained for the first time. Next, based on such fingerprint data for CLJ, various chemometrics analysis methods were applied to evaluate intrinsic quality and to identify chemical markers most responsible for quality. Finally, through comprehensive analysis, seven chemical compounds – 5-caffeoylquinic acid, 1,3-O-dicaffeoylquinic acid, epi-loganic acid, sweroside, loganin, vogeloside and grandifloroside – were identified as the most useful chemical markers to evaluate CLJ quality.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...