Ammonium salting out extraction with analyte preconcentration for sub-part per billion quantitative analysis in surface, ground and drinking water by flow injection tandem mass spectrometry†
Abstract
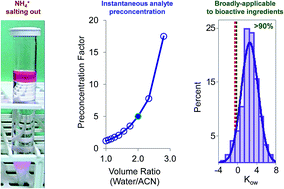
A recently-reported extraction method that merged principles of QuEChERS and salting out liquid–liquid extraction (SALLE) by using ammonium salts (chloride, acetate, formate) has been improved for high-throughput quantitation of bioactive chemicals in water by flow injection tandem mass spectrometry (FI/MS/MS). The new method for water analysis uses the ratio of acetonitrile/water adjusted to yield extract preconcentration in one step: 7.0 mL water aliquot, 3.5 mL of acetonitrile extraction solvent and 3.0 g of NH4Cl (s) resulted in post-extraction acetonitrile phase volume of 1.4 mL (extract preconcentration factor = 5). This preconcentration factor can be adjusted by changing the acetonitrile/water aliquot ratio to achieve the desired sensitivity while optimizing method performance. The acetonitrile/water partition coefficients (Kaw) of analytes in the acetonitrile/water/NH4Cl ternary systems were measured during method development. Kaw values were used to predict analyte recoveries when the acetonitrile/water ratios were varied in the extraction procedure. The effect of aqueous system pH was evaluated and the results were used for extraction optimization. A validation study was successfully conducted in creek, pond, ground, and drinking water for the following pesticides: aminocyclopyrachlor methyl, azimsulfuron, chlorantraniliprole, chlorimuron ethyl, chlorsulfuron, cyantraniliprole, diuron, flupyrsulfuron methyl, hexazinone, oxamyl, methomyl, sulfometuron methyl, triflusulfuron methyl. The method met the stringent 0.1 μg L−1 (ppb) limit of quantitation (LOQ) specified by the European Union for 10 out of 13 pesticides tested. The LOQ for the 3 least responsive analytes, i.e. chlorsulfuron, oxamyl and methomyl, was 0.3 μg L−1. Limits of detection (LODs) were between 10 and 100 ng L−1 (ppt). FI/MS/MS acquisition time was 30 seconds/injection. The correlation between analyte recoveries and publicly-available physicochemical properties, such as octanol/water partition coefficients (Kow) and aqueous solubility, was also assessed, allowing the prediction of method applicability to other chemicals, such as pharmaceuticals and other pesticides not tested in the study.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...