Metal nanoparticle assisted polymerase chain reaction for strain typing of Salmonella Typhi†
Abstract
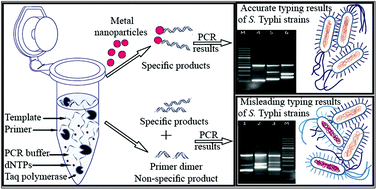
Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi (S. Typhi) is the causative agent of typhoid fever and remains a major health threat in most of the developing countries. The prompt diagnosis of typhoid directly from the patient's blood requires high level of sensitivity and specificity. Some of us were the first to report PCR based diagnosis of typhoid. This approach has since then been reported by many scientists using different genomic targets. Since the number of bacteria circulating in the blood of a patient can be as low as 0.3 cfu ml−1, there is always a room for improvement in diagnostic PCR. In the present study, the role of different types of nanoparticles was investigated to improve the existing PCR based methods for diagnosis and strain typing of S. Typhi (targeting Variable Number of Tandem Repeats [VNTR]) by using optimized PCR systems. Three different types of nanoparticles were used i.e., citrate stabilized gold nanoparticles, rhamnolipid stabilized gold and silver nanoparticles, and magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. The non-specific amplification was significantly reduced in VNTR typing when gold and silver nanoparticles were used in an appropriate concentration. More importantly, the addition of nanoparticles decreased the non-specificity to a significant level in the case of multiplex PCR thus further validating the reliability of PCR for the diagnosis of typhoid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...