Glucose-sensitive nanofiber scaffolds with an improved sensing design for physiological conditions†
Abstract
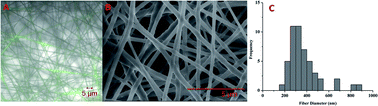
Continuous physiological monitoring of electrolytes and small molecules such as glucose, creatinine, and urea is currently unavailable but achieving such a capability would be a major milestone for personalized medicine. Optode-based nanosensors are an appealing analytical platform for designing in vivo monitoring systems. In addition to the necessary analytical performance, such nanosensors must also be biocompatible and remain immobile at the implantation site. Blood glucose in particular remains a difficult but high-value analyte to monitor continuously. Previously, we developed glucose-sensitive nanosensors that measure glucose by a competitive binding mechanism between glucose and a fluorescent dye to 4-carboxy-3-fluorophenyl boronic acid. To improve the sensitivity and residency time of our reported sensors, we present here a series of new derivatives of 4-carboxy-3-fluorophenyl boronic acid that we screened in a macrosensor format before translating into a nanofiber format with electrospinning. The lead candidate was then implanted subdermally and its residency time was compared to spherical nanosensor analogues. The nanofiber scaffolds were markedly more stable at the implantation site whereas spherical nanosensors diffused away within three hours. Based on the enhanced sensitivity of the new boronic acids and the residency time of nanofibers, this sensor configuration is an important step towards continuous monitoring of glucose and other analytes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...