Optoelectronic properties of polythiophene thin films and organic TFTs fabricated by oxidative chemical vapor deposition
Abstract
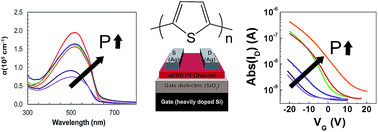
Fabrication of devices utilizing unsubstituted polythiophene (PT) has received limited attention because thin films of this insoluble material have been difficult to prepare using traditional solution-based methods. However, since the thiophene monomer is volatile, PT films can be readily fabricated by oxidative chemical vapor deposition (oCVD). The pressure of the oCVD process is here shown to significantly affect the optoelectronic properties of the PT films. Shifts in the Raman bands near 1500 cm−1 suggest that the lowest pressure deposition conditions (1 mTorr) result in shorter conjugation. Additionally, relative Raman peak intensities suggest that the polymer chains in these films contain more distortions than films deposited at higher pressures. UV-Vis absorption spectra of the oCVD PT films show that films deposited at the lowest pressure considered (1 mTorr) are slightly blue-shifted and demonstrate lower absorption than films deposited at higher pressures. PT films deposited at 75, 150, and 300 mTorr demonstrated similar UV-Vis absorption spectra, with absorption maxima near 515 nm. Organic thin film transistors (TFTs) were fabricated using oCVD PT as the active channel layer to analyze the effect of deposition pressure on charge transport and electrical properties. Films deposited at 150 mTorr demonstrate the greatest field effect carrier mobility of 4 × 10−3 cm2 V−1 s−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...