Sol–gel synthesized, low-temperature processed, reduced molybdenum peroxides for organic optoelectronics applications†
Abstract
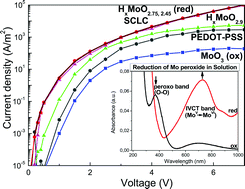
Reduced molybdenum peroxides with varying degrees of reduction were synthesized following a modified sol–gel peroxo method and the respective films were employed as anode interfacial layers in organic optoelectronics applications, such as organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) and organic photovoltaics (OPVs). The degree of reduction was controlled through both the synthesis route and the thermal treatment protocol of the obtained films. The films were thoroughly investigated with a variety of spectroscopic, diffraction, and electron microscopy methods (UV-Vis, FT-IR, XPS, UPS, Raman, XRD, SEM, and TEM). These films were found to be considerably sub-stoichiometric with a relatively high content of hydrogen. When they were used as anode interfacial layers in OLED and OPV devices, high efficiencies and adequate temporal stability were achieved. The enhanced hole injection/extraction properties of the reduced molybdenum peroxide films were attributed to the improved charge transport facilitated through the gap states present in these materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...