A new Cu–cysteamine complex: structure and optical properties†
Abstract
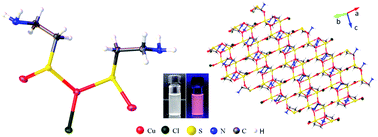
Here we report the structure and optical properties of a new Cu–cysteamine complex (Cu–Cy) with a formula of Cu3Cl(SR)2 (R = CH2CH2NH2). This Cu–Cy has a different structure from a previous Cu–Cy complex, in which both thio and amine groups from cysteamine bond with copper ions. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance results show that the oxidation state of copper in Cu3Cl(SR)2 is +1 rather than +2. Further, Cu3Cl(SR)2 has been observed to show intense photoluminescence and X-ray excited luminescence. More interesting is that Cu3Cl(SR)2 particles can produce singlet oxygen under irradiation by light or X-ray. This indicates that Cu3Cl(SR)2 is a new photosensitizer that can be used for deep cancer treatment as X-ray can penetrate soft tissues. All these findings mean that Cu3Cl(SR)2 is a new material with potential applications for lighting, radiation detection and cancer treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...