Solid-state electrochromic devices: relationship of contrast as a function of device preparation parameters†
Abstract
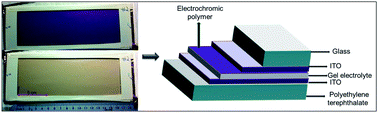
The establishment of a relationship between device performance parameters such as switch speed and photopic contrast with device composition, electrochromic polymer thickness, and gel electrolyte composition is reported here for a versatile one-step preparation method of relatively large area, 105 cm2, solid-state electrochromic devices. The electrochromic polymer, hereby, generated from a monomer after device construction, i.e. in situ, is a way to simplify the fabrication of electrochromic devices by reducing waste generation and assembly time as well as by increasing the versatility of device manufacturing in an open atmosphere. Photopic contrast is a critical property for electrochromic displays, windows, and lenses necessitating the study of how changing the selected material and device properties such as monomer diffusion, thickness of the electrochromic polymer layer, and ionic conductivity of the electrolyte impact electrochromic device functionality. More specifically photopic contrast performance is evaluated as a function of polymerization time, effective electrochromic polymer layer thickness, monomer loading, salt loading, thickness of the gel electrolyte, and in situ conversion temperature. Photopic contrasts of 47% for polybiphenylmethyloxymethyl-3,4-propylenedioxythiophene (BPMOM-ProDOT), 46% for poly2,2-dimethyl-3,4-propylenedioxythiophene (PProDOT-Me2), and 40% for poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) without background correction were achieved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...