Amorphous zinc-doped silicon oxide (SZO) resistive switching memory: manipulated bias control from selector to memristor†
Abstract
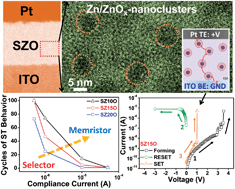
Manipulated bias control of a selector to a memristor was demonstrated in Zn-doped amorphous SiOx (SZO) films, within which ZnOx/Zn nanoclusters were segregated. For the selector, namely diode-like (pre-forming) switching, the threshold voltage varied from 9 to 2.7 V, with a resistance ratio of ∼104, by tuning the concentration of ZnOx/Zn nanoclusters. Stable bipolar resistive switching was achieved by current-controlled RESET and voltage-controlled SET processes. The working mechanism of the selector was explained by a transport mechanism which involved the “generalized trap-assisted tunnelling” of electrons resulting from doping with ZnOx/Zn nanoclusters. The dual-switching-mode of SZO provides a promising application for 3D cross-bar RRAM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...