2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and biological effects†
Abstract
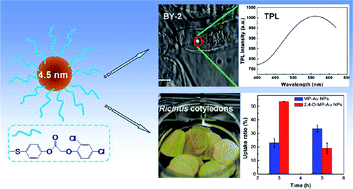
Understanding and visualizing the biodistribution of agricultural chemicals inside cells and living plants is very important for enhancing targeting and changing the application approaches of chemicals. Here, a novel material was synthesized through 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid functionalized small gold nanoparticles (2,4-D-MP-Au NPs). The successful modification of Au NPs (4.46 ± 0.70 nm) was ascertained by UV-vis, TEM, FTIR and XPS. TGA data revealed about 1197 molecules of 2,4-D were coupled to the surface of one Au nanoparticle, which was sufficient for bioapplications. The optical imaging of 2,4-D-MP-Au NPs inside BY-2 cells was directly examined, revealing that 2,4-D-MP-Au NPs could be internalized in BY-2 cells by the two-photo microscopy and endocytosis, as the internalization mechanism was energy dependent for 2,4-D-MP-Au NPs. Furthermore, the biodistribution of 2,4-D-MP-Au NPs in Ricinus cotyledons was measured, revealing that 2,4-D-MP-Au NPs could enter into mesophyll cells of Ricinus cotyledons; the cell recognition was enhanced after 2,4-D conjugated Au NPs. These results indicate that the conjugates have great potential for applications on bioimaging and biolabeling for agricultural chemicals in plant physiology.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...