Self assembly of plasmonic core–satellite nano-assemblies mediated by hyperbranched polymer linkers†
Abstract
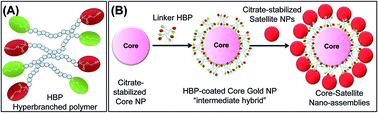
The morphology of plasmonic nano-assemblies has a direct influence on optical properties, such as localised surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) and surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) intensity. Assemblies with core–satellite morphologies are of particular interest, because this morphology has a high density of hot-spots, while constraining the overall size. Herein, a simple method is reported for the self-assembly of gold NPs nano-assemblies with a core–satellite morphology, which was mediated by hyperbranched polymer (HBP) linkers. The HBP linkers have repeat units that do not interact strongly with gold NPs, but have multiple end-groups that specifically interact with the gold NPs and act as anchoring points resulting in nano-assemblies with a large (∼48 nm) core surrounded by smaller (∼15 nm) satellites. It was possible to control the number of satellites in an assembly which allowed optical parameters such as SPR maxima and the SERS intensity to be tuned. These results were found to be consistent with finite-difference time domain (FDTD) simulations. Furthermore, the multiplexing of the nano-assemblies with a series of Raman tag molecules was demonstrated, without an observable signal arising from the HBP linker after tagging. Such plasmonic nano-assemblies could potentially serve as efficient SERS based diagnostics or biomedical imaging agents in nanomedicine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...