Antimicrobial activity of copper and copper(i) oxide thin films deposited via aerosol-assisted CVD
Abstract
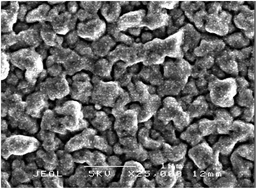
Hospital acquired infections are prevalent in many hospitals and contaminated touch surfaces are a route of transmission. To find a solution for this, copper and copper oxide thin films were deposited via aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition using copper nitrate as the precursor and the films were characterised by a range of techniques including powder X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The antimicrobial activity of the deposited copper and copper oxide films were investigated against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli). A 5-log10 reduction in the viable counts of E. coli was observed on the copper thin films after 30 minutes while a 2-log10 reduction was observed on copper oxide films after 1 hour. In the case of S. aureus both copper and copper oxide films exhibited 4-log10 reduction after 1 hour. The high antimicrobial efficacy of the Cu2O films, approaching that of the pure copper films, suggests that oxide formation on copper objects should not significantly impair their antimicrobial activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...