Zinc ferrite spinel-graphene in magneto-photothermal therapy of cancer
Abstract
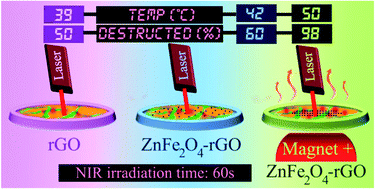
A magneto-photothermal therapy for cancer (in vitro photothermal therapy of prostate cancer cells and in vivo photothermal therapy of human glioblastoma tumors in the presence of an external magnetic field) was developed using superparamagnetic zinc ferrite spinel (ZnFe2O4)–reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanostructures (with various graphene contents). In vitro application of a low concentration (10 μg mL−1) of the ZnFe2O4–rGO (20 wt%) nanostructures under a short time period (∼1 min) of near-infrared (NIR) irradiation (with a laser power of 7.5 W cm−2) resulted in an excellent destruction of the prostate cancer cells, in the presence of a magnetic field (∼1 Tesla) used for localizing the nanomaterials at the laser spot. However, in the absence of a magnetic field, ZnFe2O4–rGO and also rGO alone (10 μg mL−1) resulted in only ∼50% cell destruction at the most in the short photothermal therapy and also in a typical radiotherapy (∼2 min gamma irradiation with a dose of 2 Gy). The minimum concentrations required for the successful application of the nanostructures in the photothermal and radiotherapeutic methods were found to be ∼100 and 1000 μg mL−1, while in the proposed magneto-photothermal therapy it was only ∼10 μg mL−1. The in vivo feasibility of this method was also examined on mice bearing glioblastoma tumors. Furthermore, the localization of the magnetic nanomaterials injected into the tumors was studied in the presence and absence of an external magnetic field. These results will stimulate more applications of magnetic graphene-containing composites in highly efficient photothermal therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...